Autothermal LOHC-Dehydrogenation
About
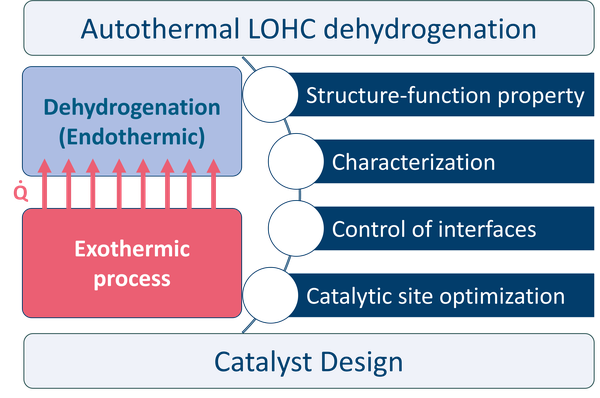
Autothermal dehydrogenation represents a cutting-edge approach in the field of chemical hydrogen storage using Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs). Our aim is to develop active, selective and robust heterogeneous catalysts that ensure excellent recyclability of LOHCs.
The focal point of our research is on the dehydrogenation reaction of LOHCs, where we seek to couple the endothermic dehydrogenation process with suitable exothermic reactions to optimize the overall energy efficiency of the chemical hydrogen storage.
Research Topics
To realize this ambitious goal, we design the topology and electronic structure of the active sites on the catalyst. This involves exerting precise control over the interfaces to develop effective immobilization strategies of printable catalyst inks or to modify the surface properties of commercial catalysts. To better understand the structure-function properties of the materials, we conduct in-depth characterization at the nano, meso, and macro scales.
The knowledge acquired is ultimately integrated to enhance the catalyst performance. Specifically, by pushing forward the intrinsic properties of the catalysts, we aim to efficiently couple the endothermic dehydrogenation process with a broad range of complementary exothermic reactions, including partial oxidation and oxidative dehydrogenation, while maintaining excellent selectivity throughout the coupled processes. This approach paves the way for more efficient management of the thermal energies involved, thereby maximizing the overall sustainability of the chemical hydrogen storage based on LOHCs.